Specifying a smart card or smart card reader may seem quite daunting as there are many Types of Smart Cards to consider:
Step 1 - Choose the type of smart card you wish to deploy?
MEMORY CARDS
Memory cards have served their markets well for many years and contain only non-volatile memory storage components. As they have no processor on the card, they can only undertake a pre-defined or fixed operation dictated by the card reader.
There are many different types of chips ranging from ones with no memory protection to fully protected read and write with encrypted communications. Memory sizes can vary with some cards offering as little as 512bits to 128Kbytes for high storage capacity.
If price is a key consideration, then memory cards tend to be less expensive than microprocessor cards, but the trade-off is that they are far less functional. Their deployment can often be more difficult as their protocols are generally proprietary compared to the more open, standardised, interfaces and protocols of microprocessor-based technology.
They are still widely used today for stored value applications such as telephone cards, vending, loyalty, access control, education and applications needing data portability but less processing capability. They have largely replaced magstripe technology in the last decade.
MICRO-CONTROLLER (MICROPROCESSOR CARDS)
Micro-controller cards, also referred as microprocessor cards, are far more versatile as they have a processor embedded with its own operating system acting like a small computer without the display and keyboard. This means the microprocessor can add, delete, and manipulate data that is already on the card, or being sent to it, for such purposes as verification, encryption, or hash generation.
As a result, they tend to be more expensive than memory cards, but their price will vary depending on their memory size, operating system, speed, and architecture.
Microprocessor cards can perform onboard cryptographic functions to improve security such as RSA, ECC, DES, AES, and algorithms such as elliptic curve are now becoming more popular.
Native V Open Platform : Integrators will need to choose between a Native or Open Platform Operating System (OS) that is running the applications on a micro-controller card.
Native OS (also known as file based) microprocessor cards conform to ISO7816 standards for commands and structure. However, some additional security or cryptographic commands can be proprietary.
Arguments against them have always been that once the development is done, the application provider is locked to that proprietary platform or vendor. Whilst this is true in many cases, that argument is lessening with some of native OS 'brands' becoming portable across multiple vendors. Card pricing as a very general rule tends to be slightly lower due to the relatively smaller licence fees compared to the open standards of Javacard and Multos. However, larger volumes are required to make production a feasible cost.
Open Platform cards such as Javacard and Multos offer extra benefits at a price premium:
- Users are not tied to single vendors. Developers can write applications that are guaranteed to run across several card vendors that support Java and Multos allowing increased choice and flexibility.
- Ease of development - smart card issuers can call on a community of application providers and re-use value added services or applets.
Step 2 - Choose which interface you need?
Contact-Only (chip insertion):

This was the traditional starting point for smart cards dating back to the late 1960's and it is the most common type in existence today. The card must be physically inserted into a smart card reader for the electrical connectors inside the reader to make connection with the chip.
Contactless Only (present card):

The fastest growing trend in the smart card world today is the uptake in 'contactless cards' due to their ease of use. The cards contain a chip & antenna inside making this invisible to the naked eye. The card uses electromagnetic induction when communicating with a smart card reader. Types of contactless cards are defined by their operating frequency.
Dual Interface (both interfaces):

As the name suggests this interface combines the best of both worlds. The cards have an embedded chip that can be used for both contact and contactless communication. The main benefit is convenience as they can be used in both scenarios. This option is not available with memory cards.
Step 3 – Visit our Online Shop for the types of available.
Memory Card / Contact Chip:
Universal Smart Cards stocks the main brands from Microchip (formerly Atmel), Fudan Microelectronics and Infineon.
There are different types of contact-only memory cards largely dictated by their level of security. Some versions contain little or no security; other versions give varying levels of protection for reading and writing data to the card.
Memory sizes can vary with some cards offering as little as 512bits to 1Mbit for high storage capacity.
Please click here our Online store where you can purchase all the leading brands for quick delivery.
If there is a particular card you cannot find, or you need further information, please give us a call and we can find it for you.
Memory Card / Contactless Only:
Contactless Cards use radio frequency identification (RFID) to communicate between the card and reader. There is a wide choice of cards in this classification due to the fact there are three common frequencies:
Low frequency (LF) 125Khz
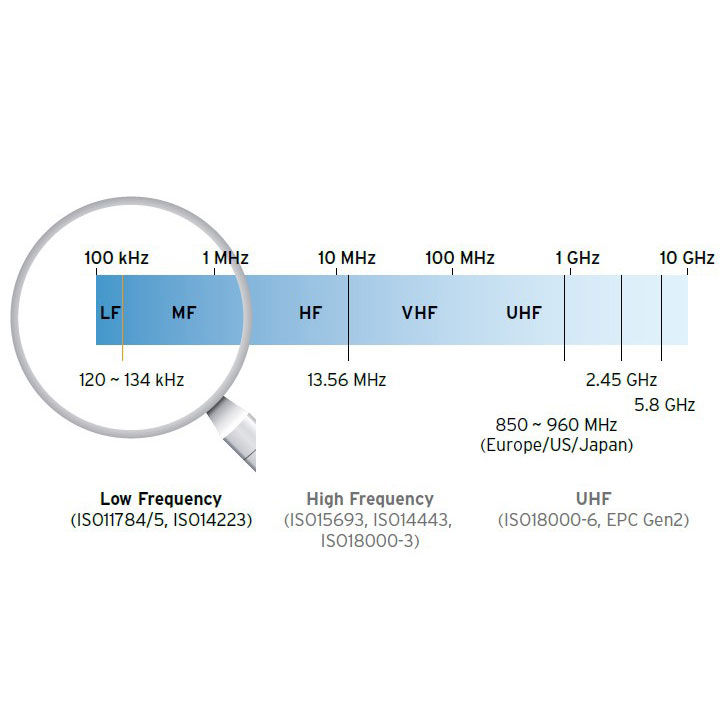
Prox Cards sprang to life in the 1990’s and are still very common today in largely physical access control systems or identification applications. As the frequency is low data exchange is limited to 64 bits enabling one-way communication between a card and a reader.
Popular brands include HID Prox, EM4102, T5557, Hitag 1 and Hitag2.
Strengths: Good reading range (up to 15cms), it is a mature market giving users plenty of choice between access control systems, installers, readers, and cards.
Negatives Cards tend to be proprietary with lots of formats from the main providers, less security, offer limited capability for multi-applications.
Universal Smart Cards stock an entire range of form factors including ISO-Sized Cards, PVC Tags, Dry & Wet Inlay, Self-Adhesive Labels, Fobs, Wristbands, and Hard Tags.
Please check our Online store where you can purchase all the leading brands for fast delivery.
If there is a particular card you cannot find, or you need further information, please get in touch and we will be pleased to help.
High frequency (HF) 13.56Mhz
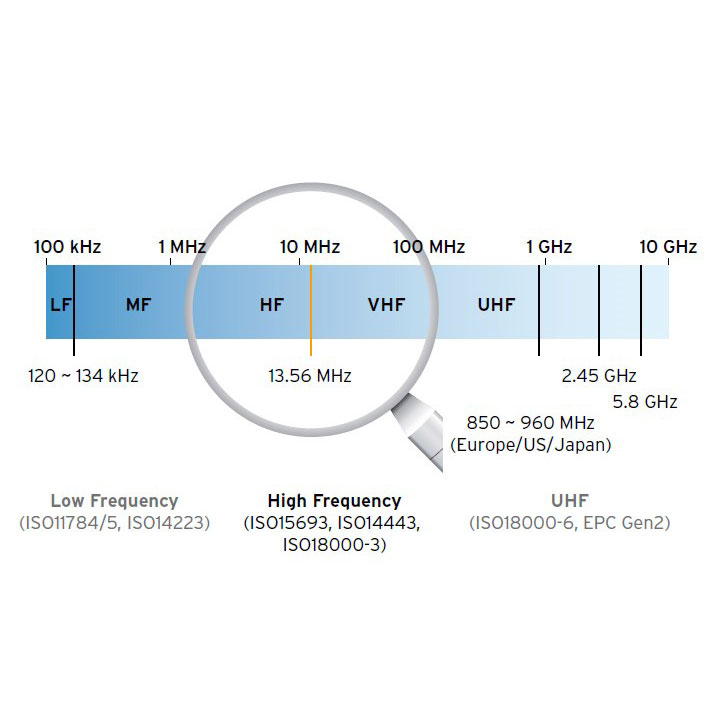
High frequency (HF) 13.56Mhz is the most diverse category for contactless Cards. They are covered by ISO/IEC 14443A/B or ISO/IEC 15693 standards. The main brands tend to offer a range of memory sizes and varying levels of security with the more secure ones offering 3DES and AES encryption. They have a medium read range of up to 10cms and higher data communication speeds make them a logical choice for applications that require secure communication and larger amounts of storage
Common brands are Mifare Ultralight, Mifare Classic, Mifare Plus, Mifare DESFire, Fudan, HID ICLASS, HID iCLASS SEOS, HID iCLASS SE, NTAG 203, NTAG 210, NTAG 210µ, NTAG 212, NTAG 213, NTAG 215, NTAG 216 and NTAG413.
Universal Smart Cards stock an entire range of form factors including ISO-Sized Cards, PVC Tags, Dry & Wet Inlay, Self-Adhesive Labels, Fobs, Wristbands, and Hard Tags.
Please check our Online Store for all these common brands most of which are normally in stock and available next day.
If there is a particular card you cannot find, or you need further information, please get in touch and we will be pleased to assist.
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF)
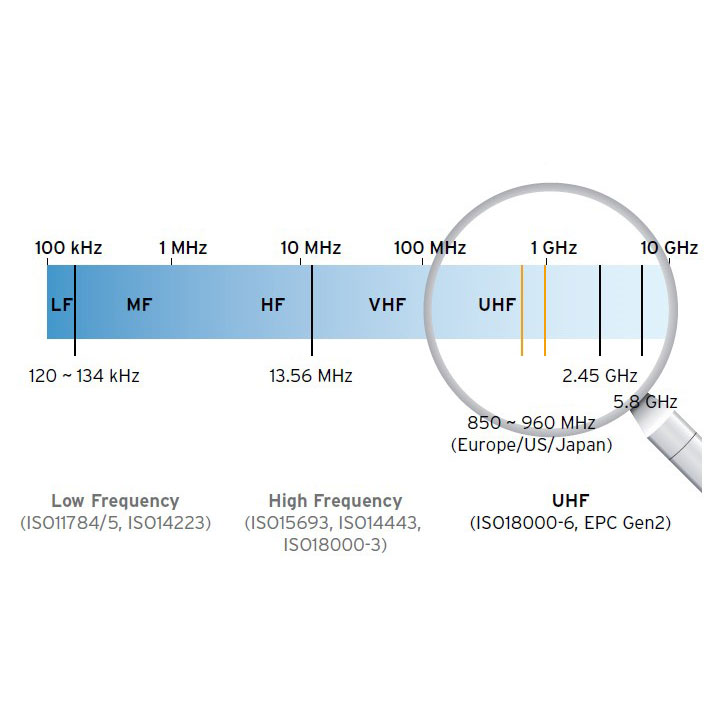
Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) follows the EPC global Gen2 standard and uses the 850-960Mhz frequency band to provide fast data transfer rates and much longer read ranges up with typical distances up to 10m. UHF labels and tags are used extensively in warehousing and goods tracking while UHF cards are popular for location and attendance tracking applications. UHF is not badly effected by materials in the environment such as metals and liquids, so it is the best choice for applications that require a long-read range, hands-free and simultaneous reading of many tags.
Common brands are Impinj Monza 4QT, Impinj Monza 4E, Impinj Monza R6, Impinj Monza RP-6, NXP Ucode 7, NXP Ucode 8 and Alien Higgs H3.
Universal Smart Cards stock an entire range of form factors including ISO-Sized Cards, PVC Tags, Dry & Wet Inlay, Self-Adhesive Labels, Fobs, Wristbands, and Hard Tags.
Please check our Online Store for all these common brands most of which are normally in stock and available next day.
Micro-Controller Cards – ALL INTERFACES
Universal Smart Cards can support both native and open platform cards with our main vendors - NXP, Infineon and HID.
A full table of the platforms we promote is shown below. All three platforms support contact, contactless and dual interface. Please click the links in the table for further information on our Smart Card Store.
| Brand | NXP | NXP | NXP | NXP | NXP | Infineon | Infineon | USC | USC |
| Product Version | JCOP | JCOP | JCOP3 | JCOP3 | JCOP4 | Oracle | SecoraID | Universal JCard | Universal JCard S |
| Product Names | (JxAyyy) | (JxDyyy) | (JxEyyy) | (JxHyyy) | (JxRyyy) | (SLJ52GDL128CR) | (SLJ52GxAyyyzS) | (C-UJC128-PSG-006) | (C-UJC080-PCG-101) |
| Java Card Version | 2.2.2 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.4 | 3.0.5 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.5 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.4 |
Global Platform | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
Max Memory | 128KB | 145KB | 145KB | 144KB | 180KB | 80KB | 120KB | 80KB | 80KB |
| Type | EEPROM | Flash | Flash | Flash | Flash | Flash | Flash | Flash | Flash |
| Extended APDU Support | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N |
| RSA | 512 - 2048 | 512 - 2048 | 512 - 2048 | 512 - 2048 | 512 - 4096 | 1024-2048 | 1024-2048 | 1024-2048 | 512-2048 |
| EC | 128 - 320 | 128 - 320 | 112 - 521 | - | 521 | 112-521 | 112-521 | 112-521 | - |
| TDES | 56, 112, 168 | 56, 112, 168 | 56, 112, 168 | 56, 112, 168 | 56, 112, 168 | 56,112,168 | 56,112,168 | 56,112,168 | 56,112,168 |
| AES | 128, 192 & 256 | 128, 192 & 256 | 128, 192 & 256 | 128, 192 & 256 | 128, 192 & 256 | 128,192 & 256 | 128,192 & 256 | 128,192 & 256 | 128, 192 & 256 |
| Mac/Hash | SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, CRC16, RIPEMD | SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, CRC16, KorenSEED, MD5, RIPEMD | SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, CRC16, CRC32, KorenSEED, MD5, RIPEMD | SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, CRC, KorenSEED | SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, CRC, KorenSEED | MAC, MAC4, MAC8, MD5, RIPEMD, SHA, SHA224, SHA254, SHA384, SHA512 | SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, CRC16 | MAC, MAC4, MAC8, MD5, RIPEMD, SHA, SHA224, SHA254, SHA384, SHA512 | MAC, MAC4, MAC8, MD5, RIPEMD, SHA, SHA224, SHA254, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 |
| MOC | N | N | N | N | Optional | N | N | N | N |
| Certification HW, SW | EAL5+ | EAL5+ | EAL5+ | EAL5+ | EAL6+ | EAL6+, EAL5+ | EAL6+ | EAL6+, EAL5+ | EAL5+, EAL4+ |
| Packaging | Contact, Contactless, Dual Interface (Bonded Module) | Contact, Contactless, Dual Interface (Bonded Module) | Contact, Contactless, Dual Interface (Bonded Module) | Contact, Contactless, Dual Interface (Bonded Module) | Contact, Contactless, Dual Interface (Bonded Module) | Contact, Contactless, Dual Interface (Bonded Module) | Contactless (Bonded Module) | Dual Interface (CoM) | Contact, Contactless (Bonded Module) |
| Further Product Information | - | - | - | Oracle’s Java CardTM operating system on Infineon’s SLE 78 | SECORA™ ID security solutions | - | - | ||
| Current Silicon Availability | > 16 weeks | > 16 weeks | > 16 weeks | > 16 weeks | > 16 weeks | > 16 weeks | > 16 weeks | > 16 weeks | > 2-4 Weeks |
| Price Range | Middle | Middle | Middle | Middle | Highest | Highest | Highest | Highest | Lowest |
| View on our website | Infineon Secora™ ID / Oracle Java™ | Infineon Secora™ ID / Oracle Java™ | Universal JCard / JCard S |
Universal Smart Cards have a stock of cards (subject to availability) that we can configure for proof-of-concept deployments and pilots.
For those wanting to explore smart card development we would recommend purchasing an evaluation kit which typically consists of hardware, tools, utilities, demos, and sample code to facilitate the development of applications. Many kits also include application tools & code samples for building a companion software piece for PCs or terminals. These are ideal for a proof-of concept, feasibility study, smart card pilot or turn-key solution.
If you cannot find what you are looking for, please get in touch and we’ll be glad to help.
For Smart Card Readers
Central to any smart card issuance in the field will be the deployment of Smart Card Readers to ‘read’ ‘write’ and 'amend' data.
As a major distributor in Europe, we are able to offer you the latest readers from the leading brand manufacturers including HID, Omnikey, Identiv, ACS and Thales.
Universal Smart Cards can supply readers for contact chip, contactless or both that are available for immediate purchase in our Smart Card Store:
Contact smart card readers:
In this instance, smart cards are manually inserted into the card reader to establish a physical electronic connection between the metal contact pad on the card itself with the reader. These types of readers support both memory and microprocessor cards.
Contactless Smart Card Readers:
These readers are becoming very popular with the ease of allowing users to simply hold their card near the surface of the reader or by simply touching it. The readers support both Low-Frequency Proximity (125Khz) and High Frequency (13.56Mhz) for reading a wide range of credentials including cards, fobs, wristbands, and tags including Near-Field Communications (NFC).
Dual Interface Smart Card Readers
Dual interface readers all comply with the relevant industry standards for contact cards (ISO7816), as well as ISO 14443 A/B and 15693 contactless standards.
Types of Smart Card & Magstripe Readers:
- Desktop/USB/Enrolment Readers- Door Access Control Readers
- Pin Pad Readers
- Magstripe Readers
- Mobile Card Readers
- SIM/SAM Readers
- OEM Modules for sub assembly
Connectivity options:







